Google Summer of Code Progress July 22#
It has been about 3 weeks after the midterm evaluations. The dipy website is gradually heading towards completion!
Dipy home page#
Progress so far#
The documentation has been completely integrated with the website and it is synced automatically from the github repository where the docs are hosted.
The honeycomb gallery in the home page is replaced with a carousel of images with content overlays that will allow us to display important announcements at the top.
The news feed now has sharing options for Facebook, Google Plus and Twitter.
Google analytics has been integrated for monitoring traffic.
There are many performance optimizations like introducing a layer of cache and enabling GZipping middleware. Now the google page speed score is even higher than the older website of dipy.
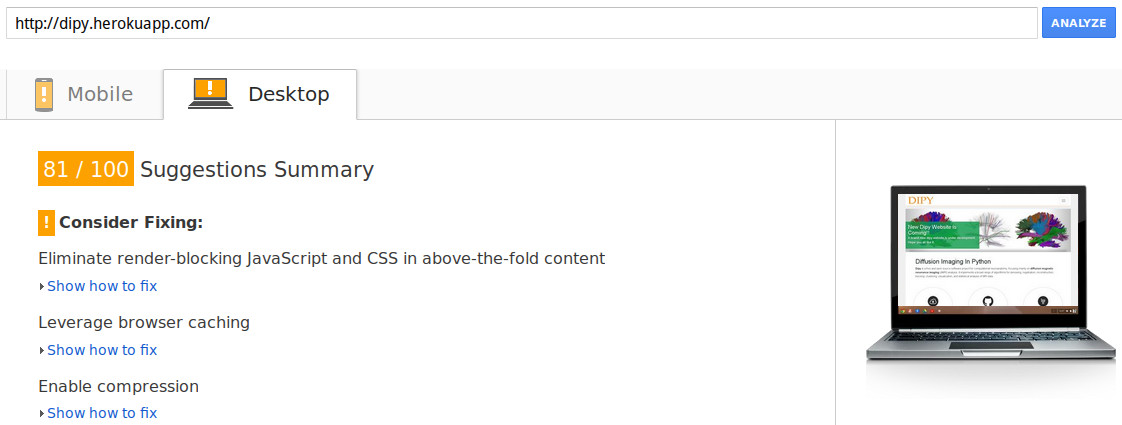
Dipy page speed#
All pages of the website have meta tags for search engine optimizations.
And of course there have been lots of bug fixes and the website scales a lot better on mobile devices.
The current pull request is #13 .
You can visit the site under development at http://dipy.herokuapp.com/
Documentation Integration#
The documentations are now generated and uploaded to the dipy_web repository using a script. Previously html version of the docs were built, but this script builds the json docs that allows us to integrate them within the django templates very easily. Then using github API the list of documentations are synced with the django website models.
def update_documentations():
"""
Check list of documentations from gh-pages branches of the dipy_web
repository and update the database (DocumentationLink model).
To change the url of the repository in which the documentations will be
hosted change the DOCUMENTATION_REPO_OWNER and DOCUMENTATION_REPO_NAME
in settings.py
"""
url = "https://api.github.com/repos/%s/%s/contents/?ref=gh-pages" % (
settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_OWNER, settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_NAME)
base_url = "http://%s.github.io/%s/" % (
settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_OWNER, settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_NAME)
response = requests.get(url)
response_json = response.json()
all_versions_in_github = []
# add new docs to database
for content in response_json:
if content["type"] == "dir":
version_name = content["name"]
all_versions_in_github.append(version_name)
page_url = base_url + version_name
try:
DocumentationLink.objects.get(version=version_name)
except ObjectDoesNotExist:
d = DocumentationLink(version=version_name,
url=page_url)
d.save()
all_doc_links = DocumentationLink.objects.all()
# remove deleted docs from database
for doc in all_doc_links:
if doc.version not in all_versions_in_github:
doc.delete()
Now the admins with proper permissions can select which documentation versions to display in the website. Those selected documentations are displayed in the navbar dropdown menu. This is done by passing the selected docs in the context in a context preprocessor.
def nav_pages_processor(request):
pages = WebsiteSection.objects.filter(section_type="page",
show_in_nav=True)
all_doc_displayed = DocumentationLink.objects.filter(displayed=True)
return {'pages_in_nav': pages, 'all_doc_displayed': all_doc_displayed}
Now when a user requests a documentation, the doc in json format is retrieved from github parsed and the urls in the docs are processed so that they work properly within the django site. Then the docs are rendered in a template.
@cache_page(60 * 30) # cache the view for 30 minutes
def documentation(request, version, path):
context = {}
repo_info = (settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_OWNER,
settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_NAME)
base_url = "http://%s.github.io/%s/" % repo_info
url = base_url + version + "/" + path + ".fjson"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 404:
url = base_url + version + "/" + path + "/index.fjson"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 404:
raise Http404("Page not found")
url_dir = url
if url_dir[-1] != "/":
url_dir += "/"
response_json = response.json()
response_json['body'] = response_json['body'].replace("src=\"",
"src=\"" + url_dir)
page_title = "DIPY : Docs %s - %s" % (version,
strip_tags(response_json['title']),)
context['meta'] = get_meta_tags_dict(title=page_title)
context['doc'] = response_json
return render(request, 'website/documentation_page.html', context)
Dipy documentation page#
Dipy documentation tutorial page#
Cache#
Processing the json documentations every time a page is requested is an overhead. Also in the home page, every time the social network feeds are fetched which is not required. So a cache is used to reduce the overhead. In django adding a cache is really really simple. All we need to do is setup the cache settings and add some decorators to the views.
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.locmem.LocMemCache',
'LOCATION': 'dipy-cache',
}
}
For now we are using local memory cache, but in production it will be replaced with memcached.
We are keeping the documentation view and the main page view in cache for 30 minutes.
@cache_page(60 * 30) # cache the view for 30 minutes
def documentation(request, version, path):
context = {}
repo_info = (settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_OWNER,
settings.DOCUMENTATION_REPO_NAME)
base_url = "http://%s.github.io/%s/" % repo_info
.... .... ... ..
But this creates a problem. When we change some section or news or publications in the admin panel then the changes are not reflected in the views and we need to wait for 30 minutes to see the changes. In order to solve the issue the cache is cleared whenever some changes are made to the sections, news etc.
class NewsPost(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
body_markdown = models.TextField()
body_html = models.TextField(editable=False)
description = models.CharField(max_length=140)
post_date = models.DateTimeField(default=timezone.now)
created = models.DateTimeField(editable=False, auto_now_add=True)
modified = models.DateTimeField(editable=False, auto_now_add=True)
def save(self, *args, **kwargs):
html_content = markdown.markdown(self.body_markdown,
extensions=['codehilite'])
print(html_content)
# bleach is used to filter html tags like <script> for security
self.body_html = bleach.clean(html_content, allowed_html_tags,
allowed_attrs)
self.modified = datetime.datetime.now()
# clear the cache
cache.clear()
# Call the "real" save() method.
super(NewsPost, self).save(*args, **kwargs)
def __str__(self):
return self.title
Search Engine Optimizations#
One of the most important steps for SEO is adding proper meta tags in every page of the website. These also include the open graph tags and the twitter card tags so that when a page is shared in a social network, it is properly rendered with the correct title, description, thumbnail etc.
The django-meta app provides very useful template that can be included to render the meta tags properly provided a meta object is passed in the context. Ideally all pages should have its unique meta tags, but there must be a fallback so that if no meta attributes are specified then some default values are used.
So in order to generate the meta objects we have this function:
def get_meta_tags_dict(title=settings.DEFAULT_TITLE,
description=settings.DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION,
keywords=settings.DEFAULT_KEYWORDS,
url="/", image=settings.DEFAULT_LOGO_URL,
object_type="website"):
"""
Get meta data dictionary for a page
Parameters
----------
title : string
The title of the page used in og:title, twitter:title, <title> tag etc.
description : string
Description used in description meta tag as well as the
og:description and twitter:description property.
keywords : list
List of keywords related to the page
url : string
Full or partial url of the page
image : string
Full or partial url of an image
object_type : string
Used for the og:type property.
"""
meta = Meta(title=title,
description=description,
keywords=keywords + settings.DEFAULT_KEYWORDS,
url=url,
image=image,
object_type=object_type,
use_og=True, use_twitter=True, use_facebook=True,
use_googleplus=True, use_title_tag=True)
return meta
And in settings.py we can specify some default values:
# default meta information
DEFAULT_TITLE = "DIPY - Diffusion Imaging In Python"
DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION = """Dipy is a free and open source software
project for computational neuroanatomy,
focusing mainly on diffusion magnetic resonance
imaging (dMRI) analysis. It implements a broad
range of algorithms for denoising,
registration, reconstruction, tracking,
clustering, visualization, and statistical
analysis of MRI data."""
DEFAULT_LOGO_URL = "http://dipy.herokuapp.com/static/images/dipy-thumb.jpg"
DEFAULT_KEYWORDS = ['DIPY', 'MRI', 'Diffusion Imaging In Python']
# django-meta settings
META_SITE_PROTOCOL = 'https'
META_SITE_DOMAIN = 'dipy.herokuapp.com'
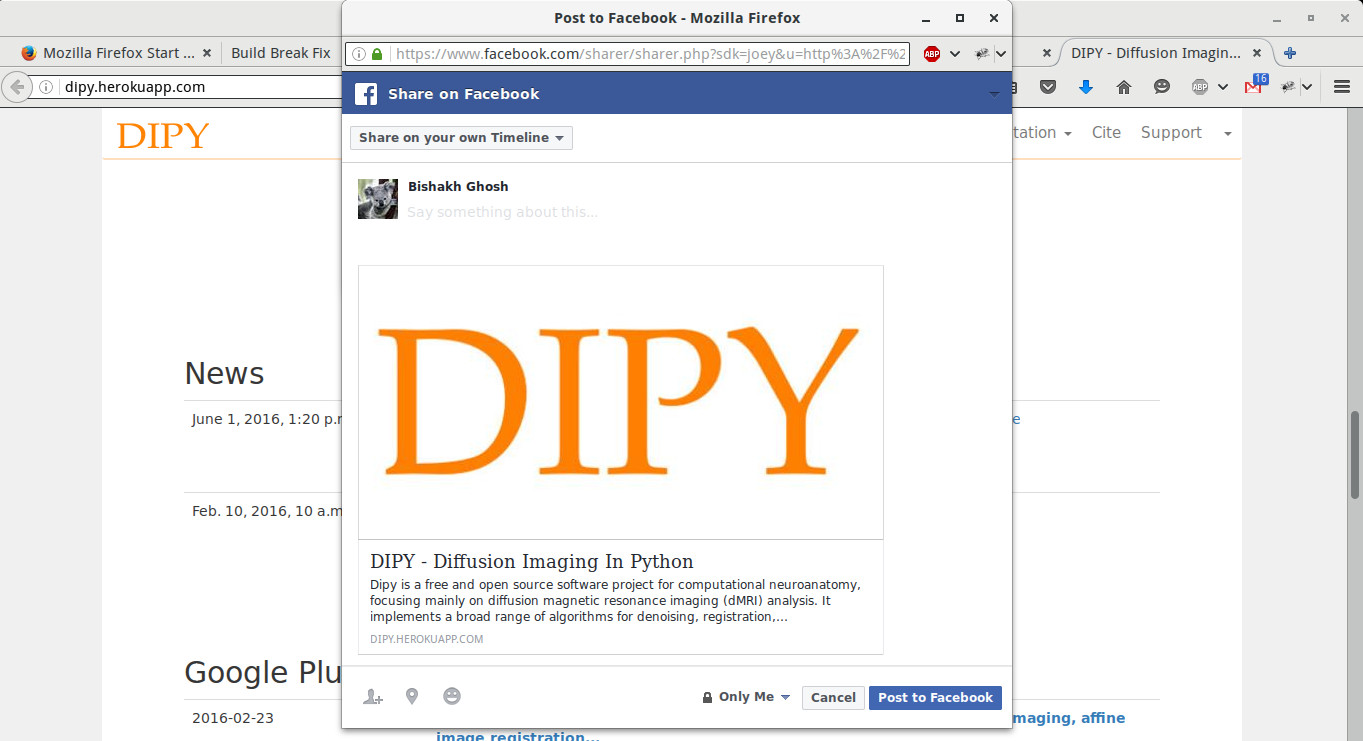
Dipy SEO share#
Google Analytics#
Adding google analytics is very simple. All we need to do is put a code snippet in every template or just the base template that is extended by all other templates. But in order to make it more easy to customize, I have kept it as a context preprocessor that will take the Tracking ID from settings.py and generate the code snippet in the templates.
def google_analytics_processor(request):
tracking_id = settings.GOOGLE_ANALYTICS_TRACKING_ID
tracking_code = """<script>
(function(i,s,o,g,r,a,m){i['GoogleAnalyticsObject']=r;i[r]=i[r]||function(){
(i[r].q=i[r].q||[]).push(arguments)},i[r].l=1*new Date();a=s.createElement(o),
m=s.getElementsByTagName(o)[0];a.async=1;a.src=g;m.parentNode.insertBefore(a,m)
})(window,document,'script','https://www.google-analytics.com/analytics.js','ga');
ga('create', '%s', 'auto');
ga('send', 'pageview');
</script>""" % (tracking_id,)
return {'google_analytics': tracking_code}
What’s next#
We have to add more documentation versions (the older ones) and add a hover button in the documentation pages to hop from one documentation version to another just like the django documentations.
We have to design a gallery page that will contain images, videos and tutorials.
I am currently working on a github data visualization page for visualization of dipy contributors and activity in the dipy repository.
Will be back with more updates soon! :)